Speech therapy plays a vital role in helping them improve their communication skills. Speech therapy encompasses a range of techniques and exercises designed to address various speech and language disorders, such as stuttering, articulation issues, voice disorders, and language delays. This article explores the methods employed in speech therapy to enhance communication skills, providing a deeper understanding of how these techniques help individuals communicate more effectively.
The Importance of Communication Skills
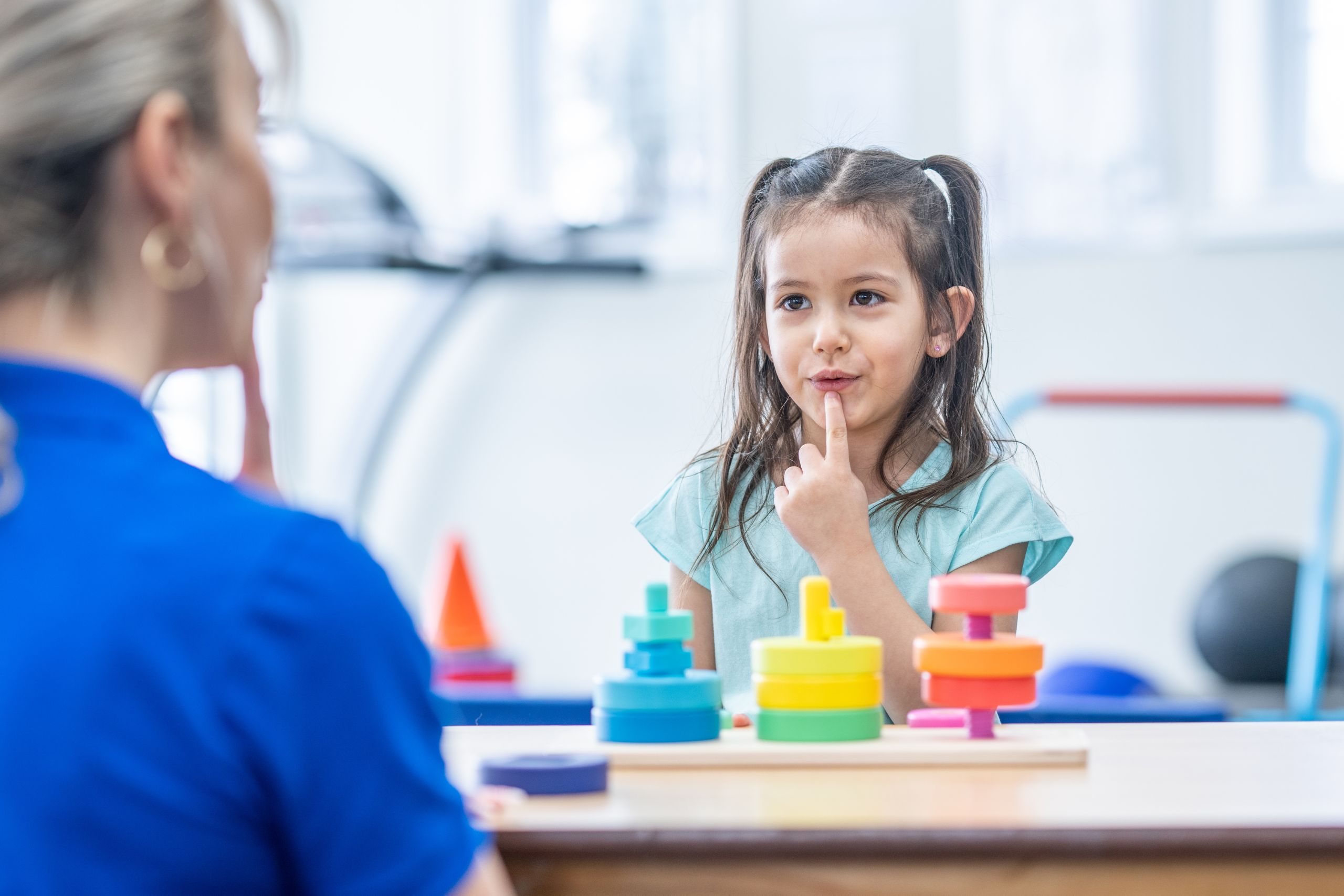

Communication skills are essential in all areas of life, from building relationships to succeeding academically and professionally. When communication difficulties arise, they can affect an individual’s confidence, social interactions, and overall quality of life. Speech therapy, therefore, is not just about fixing problems with pronunciation or grammar; it’s about improving the way a person interacts with others, processes information, and expresses themselves. Whether the challenge is a speech sound disorder, language delay, or difficulty with social communication, speech therapy offers various methods to address these issues and promote more effective communication.
Common Speech and Language Disorders Addressed in Speech Therapy
Before diving into the specific methods of speech therapy, it’s important to understand the types of communication difficulties that speech therapists work to address:
-
Articulation Disorders: Problems with producing sounds correctly, such as substituting one sound for another (e.g., saying “wabbit” instead of “rabbit”).
-
Fluency Disorders: Issues such as stuttering or cluttering, where speech flow is disrupted by unnecessary repetitions, prolongations, or hesitations.
-
Voice Disorders: Problems with the quality, pitch, or volume of the voice, such as hoarseness, breathiness, or vocal fatigue.
-
Language Disorders: These can be receptive (difficulty understanding language) or expressive (difficulty using language appropriately, such as with vocabulary or grammar).
-
Social Communication Disorders: Challenges with using language appropriately in social contexts, including understanding non-verbal cues, turn-taking in conversation, and interpreting sarcasm or humor.
Methods in Speech Therapy to Enhance Communication Skills
Speech therapists utilize a wide variety of methods to address these disorders and improve communication skills. The approach varies depending on the individual’s needs, age, and the specific challenges they face. Here are some common methods employed in speech therapy:
1. Articulation Therapy
Articulation therapy focuses on helping individuals pronounce sounds correctly. This therapy is often used for children or adults who have trouble pronouncing certain sounds, such as substituting one sound for another (e.g., “sh” for “s”) or omitting sounds altogether.
-
Visual Cues and Demonstrations: The therapist may use visual cues, such as showing how the mouth moves to produce a specific sound, or use pictures to help the individual associate sounds with images.
-
Sound Practice: The therapist may have the individual practice specific sounds in isolation (e.g., saying “s” repeatedly), then progress to sounds in syllables, words, phrases, and sentences.
-
Repetition and Feedback: Repetition of sounds and words in various contexts is critical, and therapists often provide immediate feedback to correct mispronunciations.
This method helps individuals make more accurate sounds, improving clarity in speech and enhancing their ability to communicate effectively.
2. Fluency Therapy
For those with fluency disorders, such as stuttering, speech therapy focuses on techniques that help improve the flow of speech and reduce disruptions. The main goals are to help individuals speak more smoothly and with confidence.
-
Breathing Techniques: One of the most common methods is teaching controlled breathing. Deep, slow breaths help reduce the tension that can contribute to stuttering and ensure smooth speech production.
-
Pausing and Phrasing: Teaching the person to pause briefly between words or phrases can help regulate speech flow and reduce hesitation. This strategy allows the speaker to gain more control over their speech.
-
Desensitization: This technique involves gradually exposing the person to speaking situations that may cause anxiety, helping them become more comfortable with speaking in different contexts without fear of stuttering.
Through fluency therapy, individuals learn to speak with greater ease and reduce the frustration that often accompanies disfluent speech.
3. Voice Therapy
Voice disorders, such as hoarseness or vocal strain, can significantly impact an individual’s ability to communicate clearly. Voice therapy focuses on improving the pitch, volume, and quality of the voice.
-
Breathing Exercises: Similar to fluency therapy, voice therapy often incorporates breathing exercises to improve vocal control and reduce strain on the vocal cords.
-
Pitch Modification: The therapist may work with the individual to adjust the pitch of their voice, ensuring it is neither too high nor too low, and encouraging a comfortable vocal range.
-
Vocal Warm-ups: Just as athletes warm up their muscles before exercise, individuals with voice disorders may engage in vocal warm-up exercises to prepare their vocal cords for speaking.
-
Hydration and Vocal Hygiene: Therapists often emphasize the importance of staying hydrated and practicing good vocal hygiene, such as avoiding shouting or excessive whispering.
By addressing the physical aspects of voice production, voice therapy enables individuals to use their voices in a healthier and more effective way.
4. Language Therapy
Language therapy is essential for individuals who have difficulty understanding or using language. This includes both receptive language (understanding what others are saying) and expressive language (using words and sentences appropriately). The goal of language therapy is to improve communication by enhancing the ability to process and use language effectively.
-
Vocabulary Building: Speech therapists may work on expanding an individual’s vocabulary, teaching new words and their meanings through repetition and context-based exercises.
-
Sentence Structure: For individuals struggling with grammar or sentence formation, therapists help them understand how to form complete sentences, use correct tenses, and structure thoughts clearly.
-
Language Games and Activities: Fun activities, such as story-telling exercises or word games, are often used to engage the individual while practicing language skills.
-
Social Skills Training: This involves teaching individuals how to use language in social contexts, including greetings, turn-taking, and appropriate responses to others’ comments.
Language therapy can help individuals improve their ability to understand and produce language, making it easier to communicate with others in both formal and informal settings.
5. Social Communication Training
Individuals with social communication disorders may have difficulty understanding the social rules of communication, such as how to start and maintain conversations, interpret body language, or engage in back-and-forth dialogue. Speech therapists work on improving these skills through:
-
Role-Playing: Role-playing exercises help individuals practice appropriate social interactions, such as greeting someone, making small talk, or discussing emotions.
-
Non-Verbal Communication: A significant part of social communication involves non-verbal cues, such as facial expressions, eye contact, and body language. Speech therapists may teach individuals to recognize and respond to these cues.
-
Turn-Taking Exercises: Social communication often involves taking turns in conversation. Practicing this skill in structured activities helps individuals understand the flow of communication in social settings.
-
Storytelling and Conversational Skills: Therapists often encourage individuals to practice telling stories or engaging in casual conversations, helping them structure their ideas and express themselves clearly.
Through social communication training, individuals with social communication challenges can build confidence in their interactions and enhance their ability to connect with others.
Conclusion
Speech therapy plays a crucial role in enhancing communication skills for individuals with speech, language, and social communication disorders. The variety of methods employed—ranging from articulation therapy and fluency techniques to voice therapy, language training, and social communication strategies—ensures that therapy is personalized to meet the specific needs of the individual. By working with a skilled speech therapist, individuals can improve their ability to communicate effectively, build confidence, and ultimately enhance their quality of life. Whether it’s a child learning to articulate sounds correctly or an adult managing a stutter, speech therapy provides valuable tools that empower individuals to overcome communication barriers and express themselves with clarity and confidence.